What is Hepatitis C?
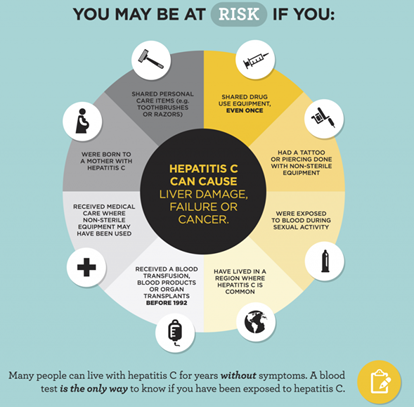
Hepatitis C, sometimes called hep C or HCV, is a virus carried in the blood which infects and can damage the liver, causing inflammation (swelling and tenderness). The liver is an important organ in the body that processes nutrients from food, filters the blood, and helps fight infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, it cannot work as well as usual.
Acute hepatitis C occurs within the first 6 months following infection with the virus. Infection does not usually cause symptoms at this stage, so many people are unaware that they have been infected. If 100 people were infected with hepatitis C, around 25 would clear the virus during the first 6 months. The other 75 would develop chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis C is an infection that lasts longer than 6 months. Over time, the virus can damage the liver, and this can cause scarring of the liver (fibrosis) and then a hardening of the liver (cirrhosis). Some people with advanced cirrhosis will develop liver failure, liver cancer or will need a liver transplant.
